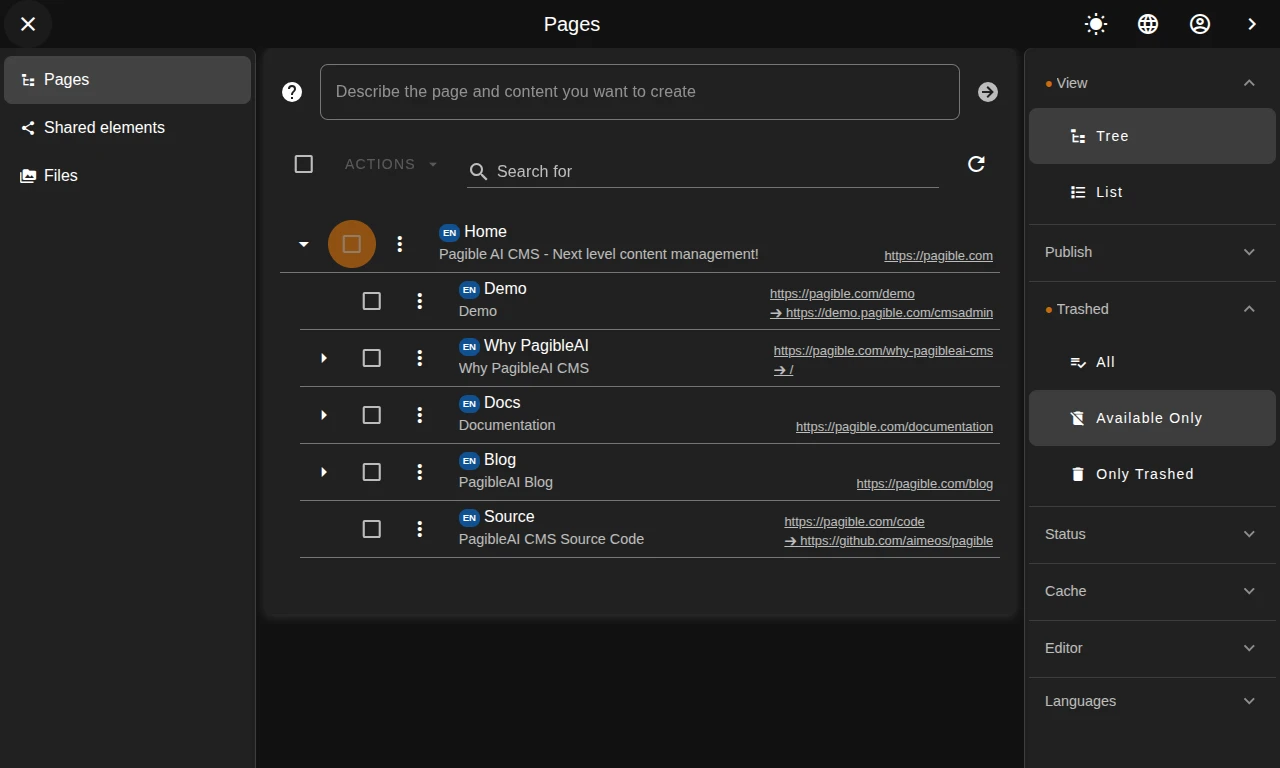
Generate content drafts from your ideas effortlessly using the built-in AI to accelerate your workflow.
PagibleAI: The Future of CMS
The first CMS build on AI with the ease of Wordpress and the power of Contentful!
Get started
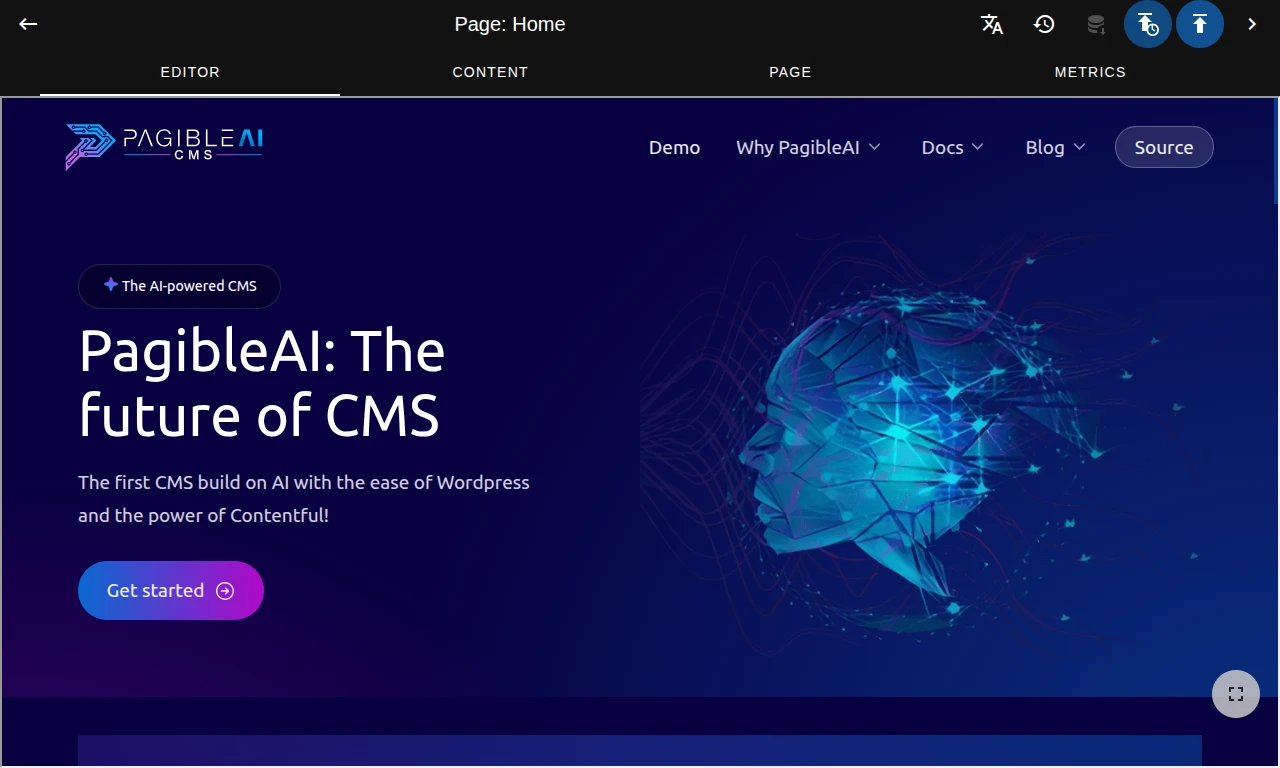
PagibleAI's Powerful Features for Editors
Your ideas generate content with AI
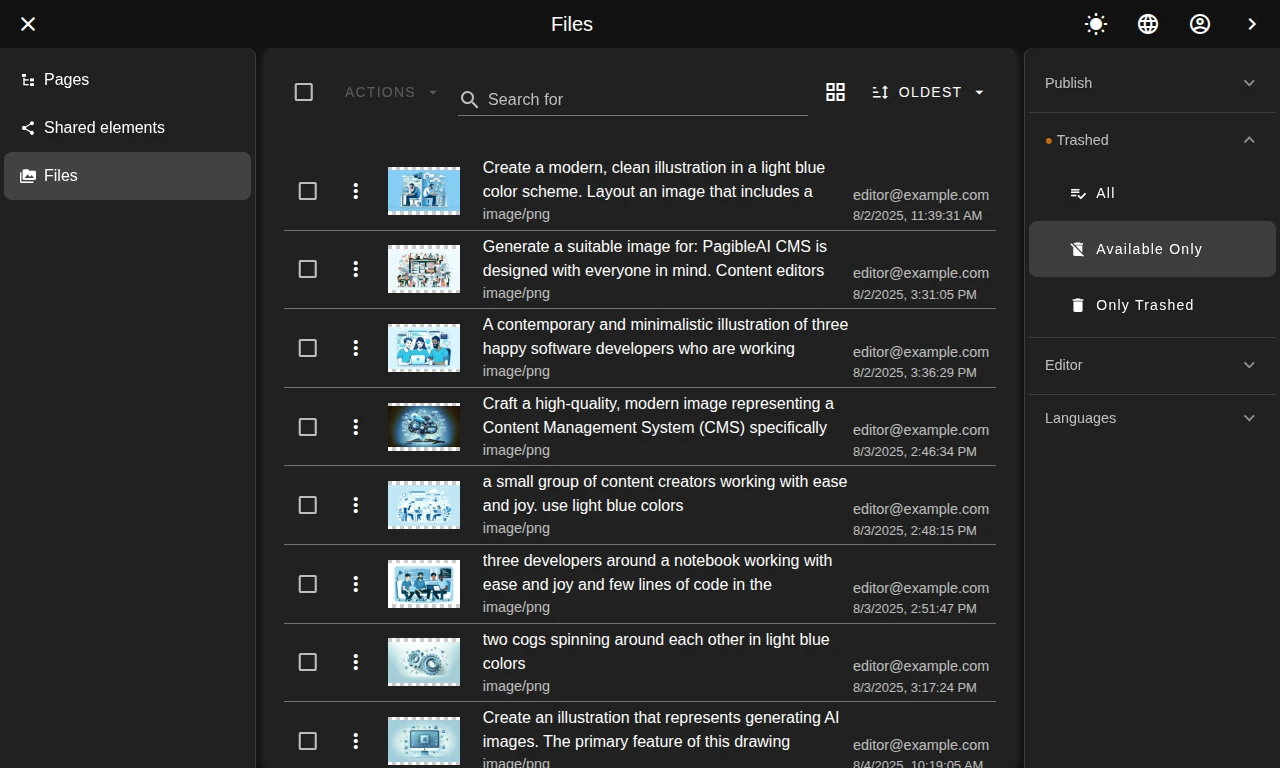
Elevate content with AI visuals
Generate perfect, visually appealing AI images to complement your content with ease.
Global reach with 35+ languages
Expand your reach with AI-powered translations, making your content accessible in over 35 languages.
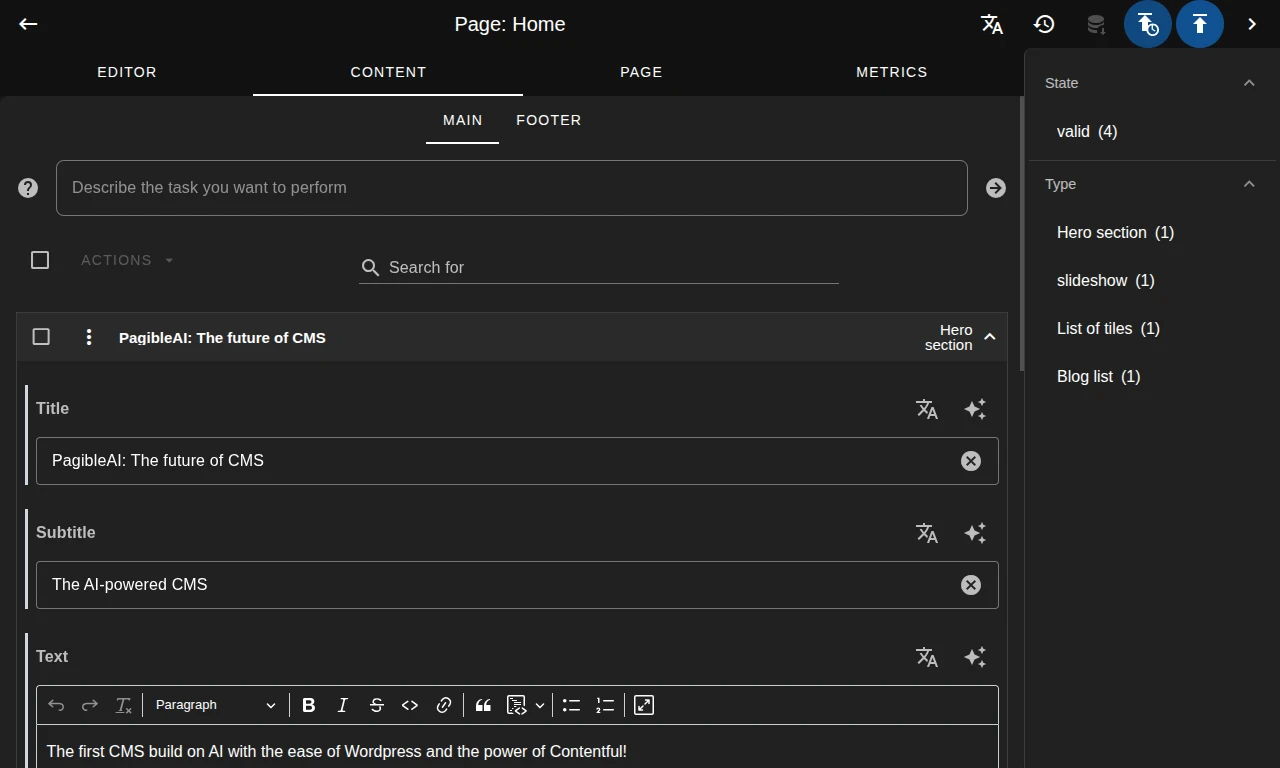
Edit content easily with WYSIWYG
Experience seamless content creation with a full WYSIWYG editor for immediate content preview.
Work efficiently with your content
Intuitive drag&drop of pages and content elements allows efficient reordering and simplifies management.
Refine and control your content
Maintain control with the ability to save drafts, publish updates, and revert to previous versions as needed.
For you in your Language
Multi-language admin backend for content management in one of 35+ languages incl. RTL support.
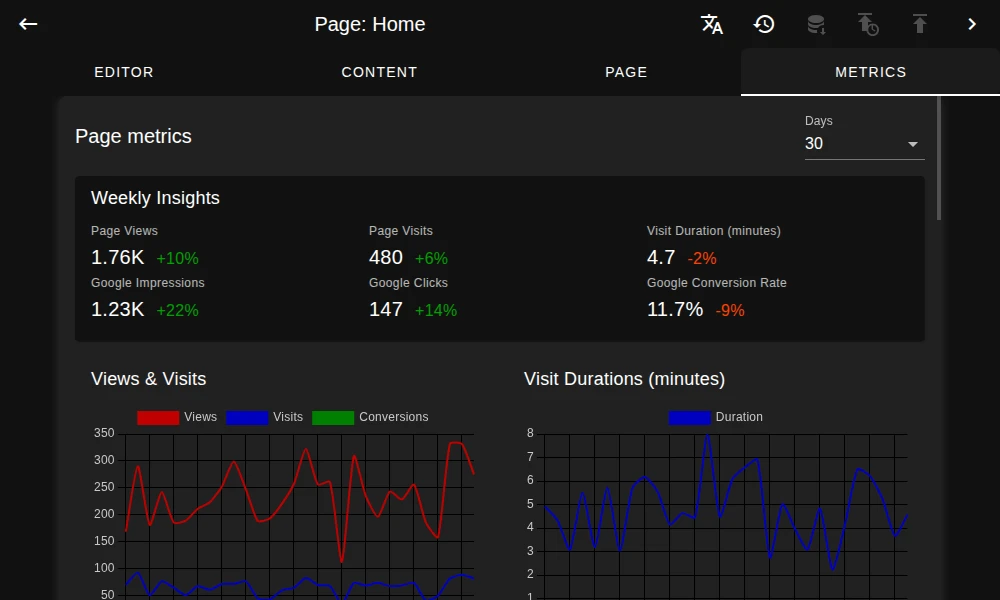
Gain valuable insights on-page
Use integrated analytics to analyze your content performance to optimize your content strategies.
Optimize content and boost visibility
See how users discover your pages through comprehensive data directly from Google Search Console.
Discover PagibleAI for Developers
Built on Laravel & VueJS
Get access to thousands of packages from the powerful and feature-rich Laravel and Vue.js ecosystems.
Extremely fast JSON REST API
Experience lightning-fast performance and unmatched efficiency with our cutting-edge JSON REST API.
Versatile GraphQL admin API
Use the power of a flexible GraphQL admin API to effortlessly manage your content from everywhere.
API or templates: Your choice
The hybrid approach offers first class API or traditional templates with themes for complete flexibility.
Multi-Channel Support
Manage structured content efficiently to maintain content for websites, mobile apps and print easily.
Multi-domain support
Manage multiple websites from one CMS instance, streamlining your content management process.
Cloud-native application
Designed to leverage the elasticity and distributed nature of AWS, Google Cloud, Azure and Kubernetes.
Extremely scalable application
Scales from simple blogs using SQLite to largest business websites with massive content and traffic.
Open Source application
Benefit from the transparency, community support, and customization possibilities of our CMS.
Why choose PagibleAI CMS?
Features
PagibleAI
Contentful
WordPress
AI-powered content
Ease of use
API-first
Structured content
Content preview
Multi-channel
Multi-language
Collaboration features
Learning curve
Customizable
Cloud-native
Scalability
Performance
Costs
No Vendor lock-in
Open Source
Frequently Asked Questions
What is PagibleAI CMS?
PagibleAI CMS is a revolutionary, new, and AI-powered content management system designed to transform the way you create and manage digital content.
It significantly simplifies content generation, leveraging artificial intelligence to streamline workflows and enhance efficiency for users.
Furthermore, PagibleAI CMS boasts seamless integration capabilities, making it an ideal solution for effortlessly incorporating advanced content management features into any existing Laravel application.
How does PagibleAI compares to traditional CMS?
PagibleAI revolutionizes content management by integrating advanced AI capabilities for content generation, image creation, and multi-language translation, offering a significant leap beyond the manual processes and conventional structures of traditional CMS platforms.
Does it support WYSIWYG?
Yes, but better! PagibleAI CMS combines frontend editing with WYSIWYG while creating or changing your content. Thus, you can see your new content in the frontend immediately after saving without any additional clicks.
Together with PagibleAI's draft and publish feature, you can update your page until it's perfect and only then, make it available to the public.
How scalable is PagibleAI CMS?
PagibleAI CMS is engineered for exceptional scalability, adapting effortlessly to diverse operational demands. It seamlessly scales from personal blog on shared hosting without database, all the way up to large-scale websites in a multi-node enterprise cluster.
This robust architecture enables it to efficiently serve billions of page requests per day, ensuring optimal performance and reliability even under the heaviest traffic loads.
Is PagibleAI CMS headless?
Yes, PagibleAI CMS is designed with headless capabilities, providing both an exceptionally fast JSON REST API and a powerful GraphQL API for seamless content administration. However, we prefer to categorize it as an API-first CMS.
This distinction highlights that while it offers robust API access for ultimate flexibility, it also provides server-side page rendering. This unique feature removes the necessity to build a separate front-end application from scratch, simplifying and accelerating development.
Is PagibleAI CMS cloud-ready?
PagibleAI CMS is inherently designed for the cloud, offering unparalleled scalability and flexibility to meet diverse deployment needs.
It seamlessly integrates with and can be deployed across all leading cloud environments, including AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and various Kubernetes-based infrastructures.
This robust cloud-native architecture ensures your content management system is future-proof, high-performing, and adaptable to any enterprise demand.
Ready for the CMS AI-Revolution?
Create Content Smarter, Faster, Simpler. Upgrade to the only CMS that puts AI, scalability, and ease of use at its core!
Start now!